Fast facts on...
This publication is available upon request in alternate formats.
PDF Version
Veteran Income
Through a Statistics Canada data linkage, before-tax incomes for 42,645 Regular Force Veterans (released 1998 to 2014) were examined for their pre-release year, the average 3 year period after release and up to 16 years post-release. Taxable income was captured which excludes any disability benefits awarded by Veterans Affairs Canada (VAC) as they are tax-free.
- 1. Average Income & Sources
-
Veteran income includes earnings from a job (i.e. “Labour Market Earnings”), pensions, investments and government transfers such as employment insurance. Earnings were the largest source of Veteran income, followed by pensions.
On average, Veterans reach their pre-release incomes by the 3rd year after release (Figure 1).
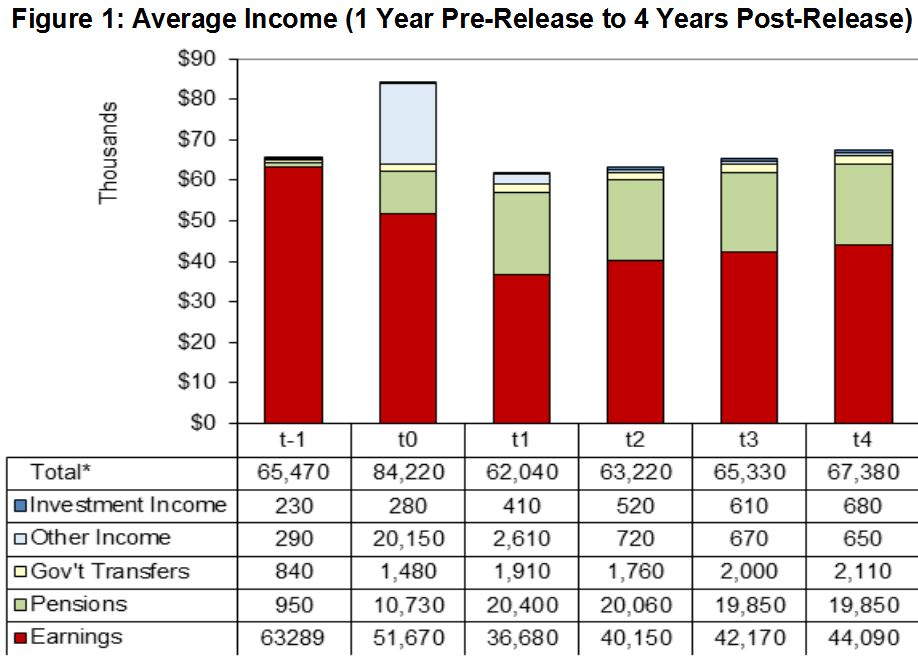
Figure 1: Average Income (1 Year Pre-Release to 4 Years Post-Release)
- 2. Labour Market Earnings (LME)
-
93% of Veterans had LME after release, but some had difficulty reaching their pre-release earnings. LME of female Veterans decreased by 58%. Veterans who completed VAC’s Rehabilitation program only replaced 50% of their LME. Younger Veterans with a disability had much lower LME replacement rates than their non-injured counterparts.
- 3. Low Income
-
Veterans were less likely than Canadians to report low income (4% vs 14%). Veterans who were more likely to experience low income at least one year post-release had released as recruits; involuntarily; or had less than 2 years of service. Older Veterans and those who released as senior officers were unlikely to experience low income.
- 4. Family Income
-
Families rely heavily on the Veteran’s income. It accounts for more than half of the total family income both before release (69%) and after release (66-70%). On average, total spousal income rose by 11% after the Veteran released from the military and their LME rose by 8%.